l5 nerve root compression test|l5 nerve root function : manufacture Lumbar radiculopathy is pain and other neurological symptoms caused by pressure on a nerve root in your lower back. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment.
Welcome to AZLyrics! It's a place where all searches end! We have a large, legal, every day growing universe of lyrics where stars of all genres and ages shine. Enter artist .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB12 de dez. de 2023 · Influencer e filha de prefeito: quem era Sofia Valim, jovem que morreu após transplante de fígado. O fisiculturista agradeceu ainda pelo apoio que recebeu dos .
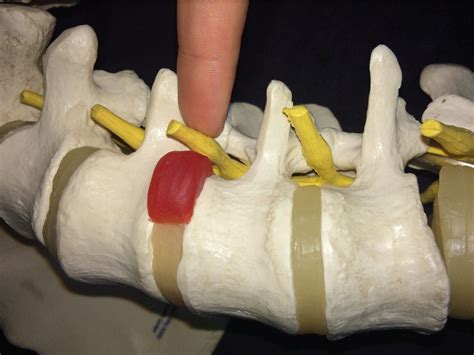
compression of lower lumbar nerve roots (L4-S1) important to distinguish from hamstring tightness. considered positive if symptoms produced with leg raised to 40°. crossed straight leg raise. performing straight leg raise .Lumbar radiculopathy is usually caused by compression of a lumbar nerve root, resulting in symptoms which radiate down the legs. It causes at least one of the following: decreased .Conditions. Spine Anatomy. All about L5-S1 (Lumbosacral Joint) By: David DeWitt, MD, Orthopedic Surgeon. Peer-Reviewed | Español. The L5-S1 spinal motion segment, also called the lumbosacral joint, is the transition region .Lumbar radiculopathy may occur when the spinal nerve roots are irritated or compressed by one of many conditions, including lumbar disc herniation, spinal stenosis, osteophyte formation, .
Radiculopathy is caused by a pinched nerve in your spine. More specifically, it happens when one of your nerve roots (where your nerves join your spinal column) is . Lumbar radiculopathy is pain and other neurological symptoms caused by pressure on a nerve root in your lower back. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment. Acute lumbosacral radiculopathy is a diffuse disease process that affects more than 1 underlying nerve root, causing pain, loss of sensation, and motor function depending on . Lumbosacral radiculopathy is characterized by pain resulting from compression or irritation of nerve roots in the lumbosacral region of the spine, along with numbness, weakness, and reflex changes. This condition .
Lumbar radiculopathy is characterized by radiating leg pain, abnormal sensations, and muscle weakness due to spinal nerve root compression in the lower back. Lumbar radiculopathy is pain and other neurological symptoms caused by pressure on a nerve root in your lower back. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment.
symptoms of l5 nerve compression
Nerve compression syndromes are a common cause of nerve (neuropathic) pain in the limbs. They can lead to a pinched nerve and neuropathy (nerve damage). What are the types of nerve compression syndromes? Nerve compression syndromes can affect different peripheral nerves in your upper or lower body. Syndromes that affect your upper limbs include:If certain reflexes are decreased or absent, it can show your doctor that there is pressure on a nerve root. Not all nerve roots have a reflex associated with them. The vertebrae of the spine are divided into regions: cervical (C), thoracic (T), lumbar (L), sacrum (S), and coccyx. Within each region, each vertebra is numbered.Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.. Technique [edit | edit source]. There are different ways described in the .Needle EMG is the more sensitive portion of the test and may reveal active denervation in the distribution of the involved nerve root, and neurogenic-appearing voluntary motor units in more chronic radiculopathies. . Also for patients with lumbar nerve root compression, lumbar traction as extra treatment is not superior to extension-oriented .
Types of nerve root pain include: Lumbar nerve pain (sciatica): Lumbar nerve pain can be a combination of back and leg pain, with pain worse in the leg below the knee. . Nerve root pain is often caused by other underlying conditions that have caused compression or damage to the nerve root. Causes of nerve root pain may include: Arthritis .If nerve root compression is present, this test causes severe pain in the back of the affected leg and can reveal a disorder of the L5 or S1 nerve root. A crossed straight-leg raising test may .
Another common presentation is back pain radiating into the foot, with a positive straight leg raising test.[3][4][5][6] Muscle strength is often preserved in the case of radiculopathy because muscles often receive innervation from multiple roots. . An L5 nerve root compression occurs from a central disc protrusion of L2-L3 or L3-L4, a .The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is commonly used to identify disc pathology or nerve root irritation, as it mechanically stresses lumbosacral nerve roots. It also has specific importance in detecting disc herniation and neural compression.[2] [3][4]It is also classified as a neurodynamic evaluation test as it can detect excessive nerve root tension[5] or .Sciatica describes radiating leg pain caused by inflammation or compression of the lumbosacral nerve roots (L4–S1) forming the sciatic nerve. The pain can have a sudden or slow onset, and vary in severity. It is felt in the back or buttock and radiates down the leg below the knee into the foot and toes in the distribution of the sciatic nerve.
This test may be used if your healthcare professional suspects you have nerve root compression. High-resolution ultrasound. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within the body. It's helpful for diagnosing nerve compression syndromes, such as carpal tunnel syndrome. The straight leg raise test also called the Lasegue test, is a fundamental neurological maneuver during the physical examination of a patient with lower back pain that seeks to assess the sciatic compromise due to lumbosacral nerve root irritation. This test, which was first described by Dr. Lazarevic and wrongly attributed to Dr. Lasegue, can be positive in . Lumbar Nerve Roots. There are 5 lumbar vertebrae. The lumbar nerve roots emerge from the lateral spinal recess formed by the rostral vertebrae's inferior facet and the caudal vertebra's superior facet. The L5 nerve root exits between the L5 and S1 vertebrae. Lumbar Plexus. The lumbar plexus comprises the anterior rami of spinal nerves L1 to L4.
It usually results from compression of lumbar nerve roots in the lower back. Common causes include intervertebral disk herniation, osteophytes, and narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis). . The straight leg raise test can be done while patients are seated with the hip joint flexed at 90°; the lower leg is slowly raised until the . The Lasegue sign or straight leg raise (SLR) test is a clinical test to assess nerve root irritation in the lumbosacral area.[1] This test is an integral part of the neurological examination of the patients presenting with low back pain with or without radicular symptoms. The other less commonly used name is the Lazarevic sign (see Image. Lasegue Sign).
right l5 nerve root impingement
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes examination of the L5 nerve root.Follow me on twitter:https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMCFind me on In.
Introduction. Radiculopathy refers to the compression or irritation of a spinal nerve root, causing pain with sensory changes (e.g. numbness, ‘pins and needles’) and/or motor changes (e.g. weakness, diminished deep tendon .
Foraminotomy: The opening for the spinal nerve root (intervertebral foramen) is enlarged by trimming bony overgrowth, relieving compression. Facetectomy: The facet joints are trimmed to relieve compression of nerve roots. Lumbar interbody fusion: A degenerated disc is removed and L5-S1 vertebrae are fused together with implants or bone grafts . Lumbosacral radiculopathy is characterized by pain resulting from compression or irritation of nerve roots in the lumbosacral region of the spine, along with numbness, weakness, and reflex changes. . the reverse straight leg (Ely) test stretches the femoral nerve and the L2 to L4 nerve roots by extending the hip and flexing the knee with the .Radiculopathy refers to symptoms that develop when there is compression of a spinal nerve root. Most commonly, the nerve compression is related to a disc herniation or spondylosis (degenerative changes in the spine) and may occur with or without trauma. It is important to note that not all disc herniations cause nerve compression or pain. If your compromised nerve root is in the lumbar spine, Social Security will also want to see the results of a positive "straight-leg raising test" (also known as a "Lasègue test"). Your records should also include the various treatments you have tried, such as pain medication, physical therapy, or steroid injections, as well as the side .
L4-L5 disc results in compression of the L5 nerve root. L5-S1 disc results in compression of the S1 nerve root. Associated conditions. cauda equina syndrome. . Spurling test. test by extending head, rotating and laterally bending to the affected side, and vertically compressing the head downward.
With central stenosis, there is a narrowing of the central canal of the lumbar spine that houses the spinal cord. This causes pain in both legs. With foramen stenosis, a narrowing of spaces on either side of the lumbar spine where nerve roots branch off from the spinal cord. Associated pain occurs in the affected right or left leg. In particular, more patients with upper lumbar nerve root compression (L2 to L3) would have strengthened the conclusions, as this study has only shown the slump knee bend test to be valid for L4 spinal nerve/nerve root compression. The most common is tension, irritation, or compression of a lumbar nerve root or roots. The irritation or compression may occur within or outside of the spinal canal. Intraspinal canal compressions may be caused by disc lesions, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, hypertrophic changes, or spinal malignancy.
Radiculopathy vs. spondylolysis. Spondylolysis is a weakness at the point your vertebrae (the bones that make up your spine) connect together. This can lead to small stress fractures that cause pain, usually in your lower back. It usually affects teens going through growth spurts. Radiculopathy can be caused by bones in your spine moving out of place, but .Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes examination of the S1 nerve root.Follow me on twitter:https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMCFind me on In.
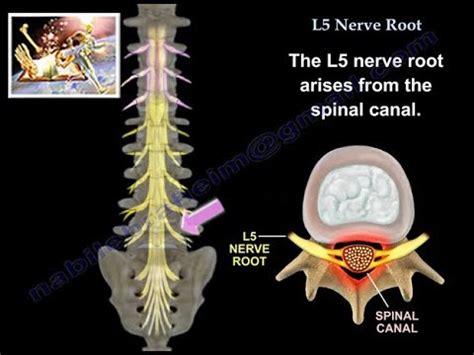
left l5 nerve root impingement
l5 nerve root irritation
Resultado da Como podem ou não saber, o Tugaflix era uma espécie de Wareztuga dos tempos atuais, em que as pessoas podiam ver séries e filmes sem terem de gastar dinheiro (eventualmente sendo isso não muito legal). Eles mudaram o site várias vezes por terem sido mandados abaixo umas quantas outras e .
l5 nerve root compression test|l5 nerve root function